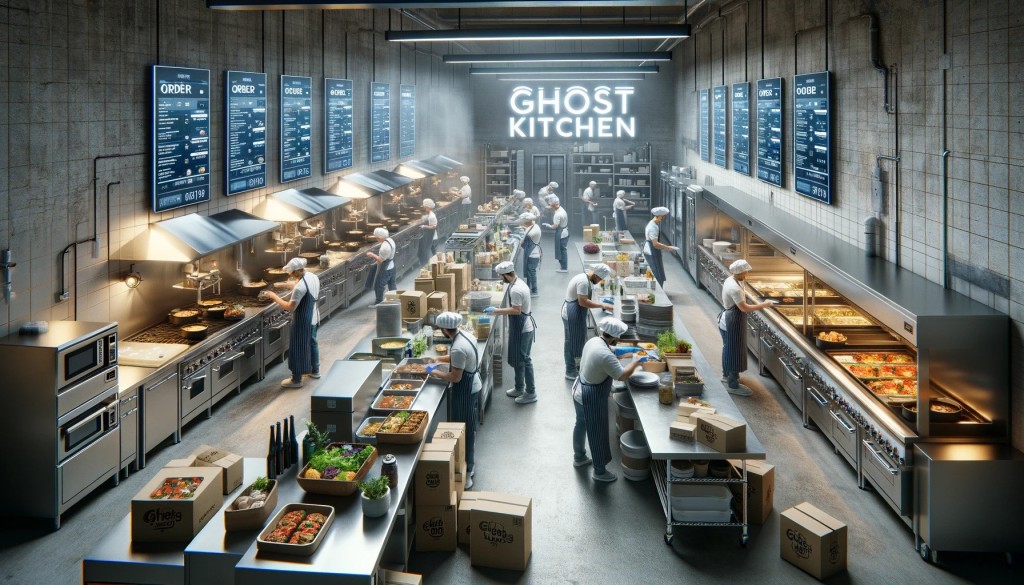
The technological landscape within the food and beverage industry, particularly in the realm of ghost kitchens and virtual restaurants, is rapidly evolving, offering unprecedented opportunities for innovation and efficiency. These advances are not just reshaping the operational aspects of these businesses but are also enhancing the customer experience in profound ways.
Automation and Robotics
One of the most significant technological advancements is the integration of automation and robotics in kitchen operations. Automated cooking appliances, robotic arms, and AI-driven systems are being deployed to increase the speed and consistency of food preparation. For instance, robotic systems can now manage tasks ranging from flipping burgers to assembling pizzas, reducing human error, and ensuring consistent product quality. This automation extends to packaging and sorting, streamlining the process from kitchen to customer.
IoT and Smart Kitchens
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming ghost kitchens into smart kitchens. Sensors and connected devices monitor equipment performance, manage inventory, and ensure food safety by tracking temperatures and hygiene levels. IoT technology also enables real-time data collection, allowing for more efficient kitchen management and operation. This connectivity ensures that equipment maintenance can be predictive rather than reactive, minimizing downtime and loss of productivity.
Advanced Delivery Logistics
Technological advancements in delivery logistics are crucial for the success of ghost kitchens and virtual restaurants. Drones and autonomous vehicles are beginning to emerge as viable delivery methods, potentially reducing delivery times and costs. Moreover, sophisticated routing algorithms and delivery management software optimize delivery routes, ensuring that food reaches customers in the shortest possible time while maintaining quality.
Personalization through AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) plays a pivotal role in personalizing the customer experience. By analyzing customer data and preferences, virtual restaurants can offer personalized menu recommendations, promotions, and meal plans. This level of personalization not only enhances the customer experience but also encourages repeat business by making customers feel understood and valued.
Deep Dive into Sustainability
Sustainability is a critical consideration for the future growth of ghost kitchens and virtual restaurants. As these models continue to gain popularity, their potential impact on the environment and local communities is being scrutinized more closely.
Reducing Food Waste
Ghost kitchens and virtual restaurants have a unique opportunity to reduce food waste through precise inventory management enabled by technology. Advanced forecasting algorithms predict demand more accurately, allowing these businesses to order and prepare food more efficiently. This precision reduces the surplus food that typically leads to waste in traditional restaurant settings.
Energy Efficiency
The centralized nature of ghost kitchens allows for more energy-efficient operations compared to traditional restaurants. By designing kitchens specifically for delivery, these facilities can optimize space and equipment usage, leading to lower energy consumption. Furthermore, investments in energy-efficient appliances and sustainable building materials further reduce the carbon footprint of these operations.
Sustainable Packaging
The reliance on delivery presents an environmental challenge due to the increased use of packaging. However, ghost kitchens and virtual restaurants are at the forefront of adopting sustainable packaging solutions. Biodegradable, compostable, and reusable packaging options are becoming more prevalent, driven by both consumer demand for sustainability and regulatory pressures.
Local Sourcing and Community Impact
Ghost kitchens and virtual restaurants are increasingly focusing on local sourcing for ingredients, which not only supports local farmers and producers but also reduces the carbon emissions associated with long-distance food transportation. Additionally, by operating in urban areas, these businesses can contribute to local economies, providing jobs and supporting community development.
Conclusion
The integration of advanced technologies and a commitment to sustainability are key drivers in the evolution of ghost kitchens and virtual restaurants. These advancements not only improve operational efficiency and customer satisfaction but also address some of the critical challenges facing our planet. As we look to the future, the continued innovation in these areas will be crucial for the growth and acceptance of ghost kitchens and virtual restaurants as a sustainable, efficient, and customer-centric model in the food and beverage industry.